¶ Navigation and Usage
¶ SPATIAL main window
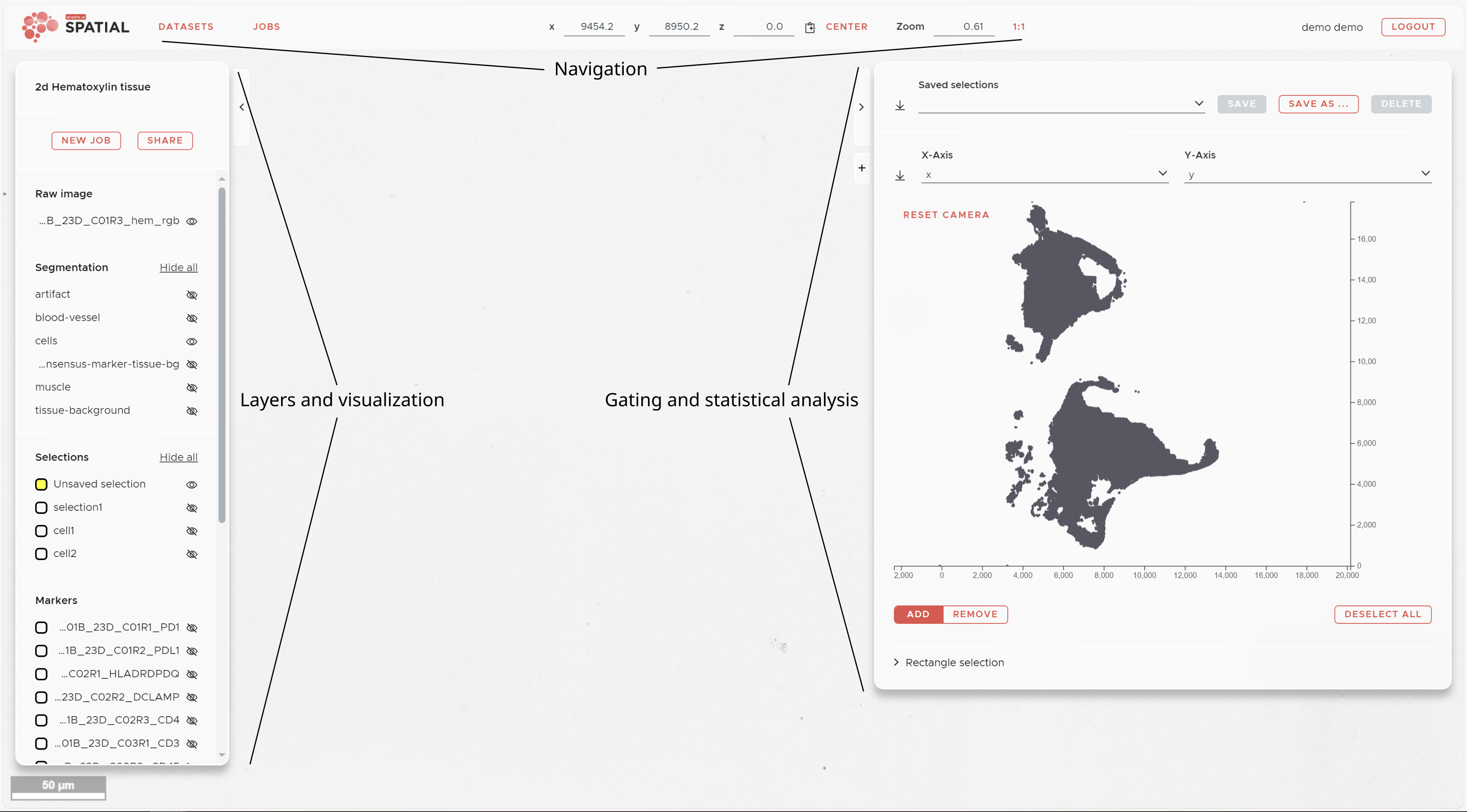
The SPATIAL main window shows 3 different panels around your image data.
On the left hand side you have the visualization panel that shows all available image, segmentation, selection and marker layers. On the right hand side you can find the Statistics panel that allows marker intensity visualization, gating and advanced statistical spatial analyses. Both panels can be collapsed using the arroheads at their top corners.
The top panel depicts the coordinates and allows you to center and resize your data using the CENTER and 1:1 buttons. The navigation panel also provides access to the job list and the datasets browser.
Most important is the NEW JOB button that allows you to submit analysis tasks to the SPATIAL software
¶ Basic usage and inputs
- Move Image: To move the displayed image press and hold down the left mouse button while moving the mouse.
- Image zoom: To enlarge or decrease the size of the displayed image, hold down the Ctrl-key on your keyboard, hover with the mouse pointer over the image and use the mouse wheel. When zooming in, SPATIAL will enlarge the region of your mouse pointer.
Be aware that SPATIAL uses a pyramidal image format loading only the necessary resolution. Depending on your connection speed you might experience small delays loading high resolution data. - Panel and font size: The panel and font size is in line with the basic zoom settings of your web browser. You can change them by pointing the mouse pointer on one of the panels (not the graph area), holding down the Ctrl-key and moving the mouse wheel.
- Jump to a location: Click with the right mouse button on a location to jump to it.
- Move along z: Use the mouse wheel to move along the z-axis.
- Paste coordinates from the system clipboard: To move to a specific location you can paste previously saved coordinates from your system clip board.
¶ Navigation panel

The navigation panel serves two main purposes. First it keeps you up to date on your current position in the dataset and lets you access specific locations. Second it provides access to the main controls of SPATIAL.
-
NEW JOB Button: Submit a new job for Registration, Segmentation, Marker mapping, a Neighborhood-enrichment score or a Recurrent spatial neighborhoods analysis.
-
SHARE Button: The SHARE button creates a sharable link that allows your dataset to be viewed by your collaborators.
-
DATASETS Button: The DATASETS button takes you to the datasets browser where you can upload new datasets or choose a different dataset.
-
X, Y and Z ccordinates: You can use the text fields of the x, y and z coordinate to enter specific locations (confirm with Enter-key). The small icon next to the z-coordinate copies the current position to the clipboard.
-
CENTER Button: The center button centers the current dataset in SPATIAL.
-
1:1 Button: The 1:1 Button sets the zoom to 1.
-
Camera icon: The camera icon makes a screenshot of the current view.
¶ Visualization panel
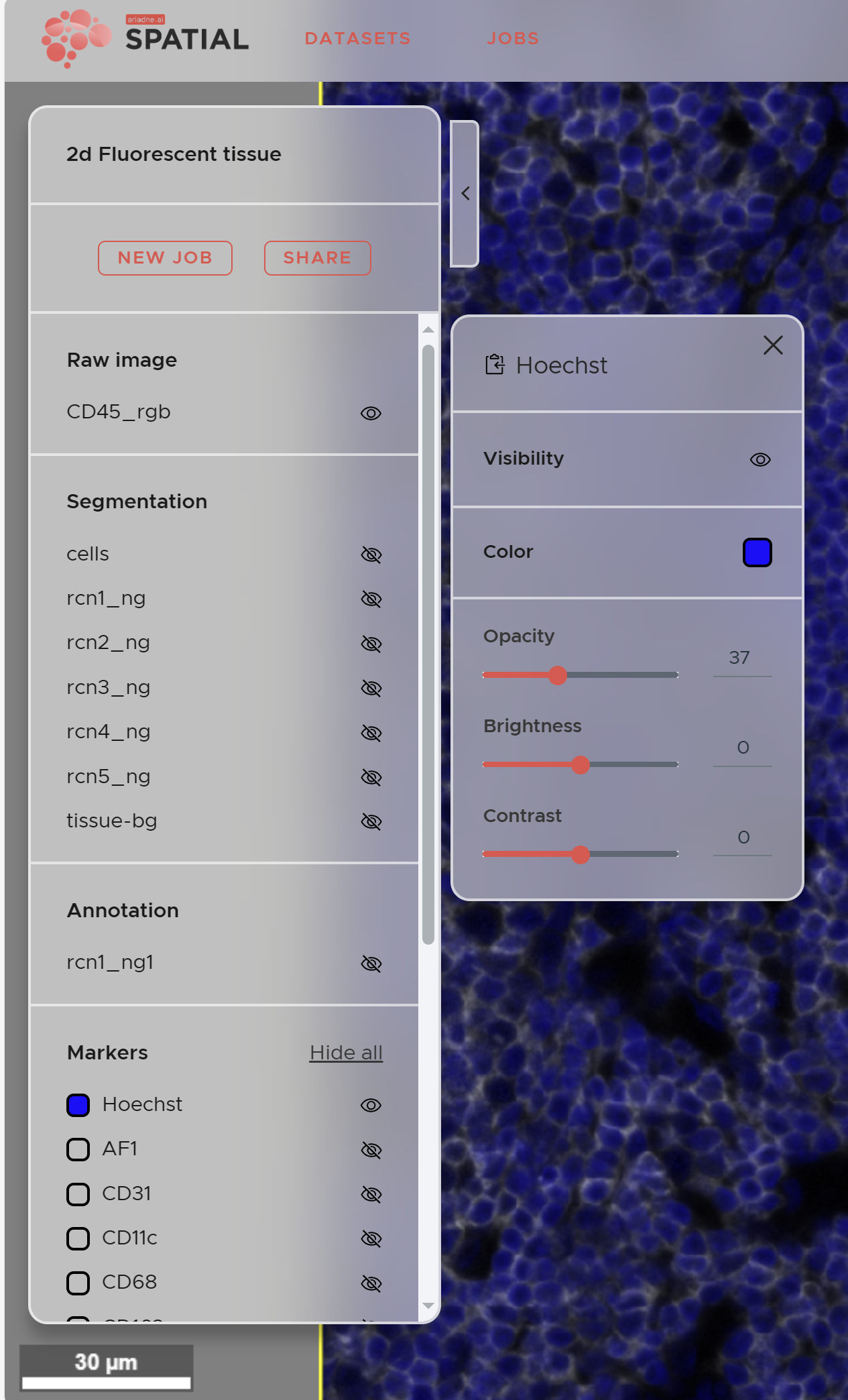
The visualization panel on the left side of the SPATIAL main window allows you to control the raw data, segmentation, selection and marker layers of your data. Depending on the state of processing and your data you might not have access to all categories yet. Missing categories like for example segmentation will appear on completion of the respective job.
- To show a specific layer click on the eye icon next to its name.
- For more options click on the layer name. Here you can set Opacity, Brightness and Contrast
- You can define the color of a marker by clicking the colored square.
¶ Gating and statistical analysis
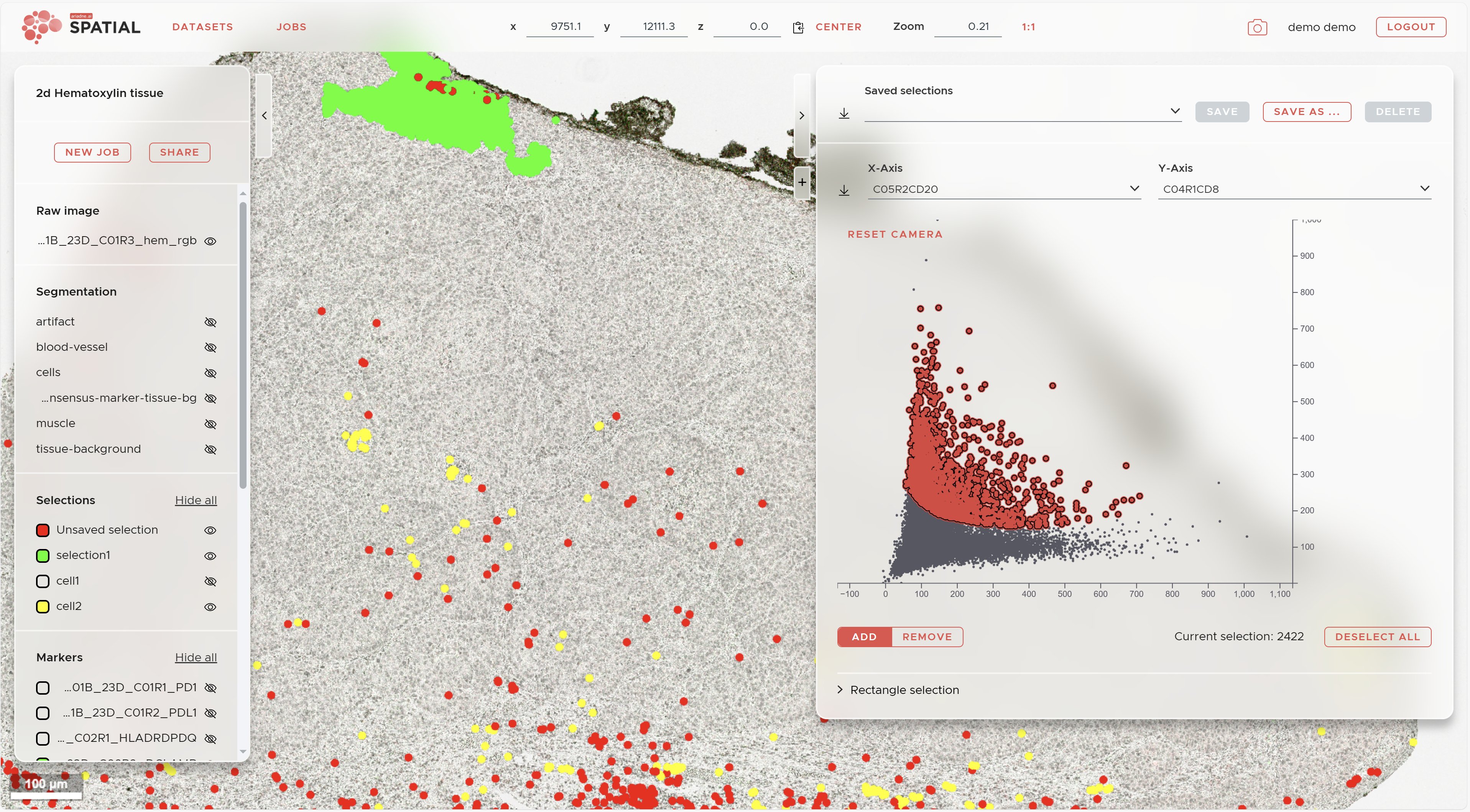
The right panel allows you to access the mapped marker intensities and make selections for cell gating. Furthermore you can access your results of the Recurrent Spatial Neighborhood (RCN) analysis.
¶ Marker intensities and Gating
To do manual cell gating use the following strategy:
- Use the 2 drop down menus for the x- and y-axes on top of the plot to select the 2 markers you want to use for gating your first cell type.
- Hold down the Shift-key and draw a region while also holding down the left mouse button. You will see a red selection appearing.
- Switch the selection mode between ADD or REMOVE using the buttons on the lower left of the plot to further refine your selection.
- To involve additional markers use again the 2 drop down menus for the x- and y-axes on top of the plot. Your current selection will be kept when selecting new markers.
- Repeat the two previous steps to refine your selection.
- Once you are done with the cell type click on the SAVE AS... Button to save it. The selection (cell type) will appear in the Selections section of the visualization panel.
- Click on the DESELECT ALL button on the lower right of the plot to start over with the next cell type.
To allow for more precise gating you can choose Rectangle selection at the bottom left of the plot and enter precise values for your gates.
Together with the mapping of markers you will be also provided automated gating using T-SNE and UMAP clustering. You can access them using the 2 drop down menus for the x- and y-axes on top of the plot.
Once you gated all your cell types go ahead and submit a Recurrent spatial neighborhood (RCN) job to analyze the tissue microenvironment in your sample.
¶ Clustering analysis (Neighborhood-enrichment)
The purpose of the Neighborhood enrichment score is to quantify the pairwise clustering of the cells based on their connectivity. Positive neighborhood enrichment score means a given pair of selections are found in each others vicinity (enriched) compared to a random distribution.
To start the neighborhood enrichment analysis, click on the NEW JOB button and select Neighborhood enrichment. To submit the neighborhood enrichment job, you need to provide the following parameters:
- Selections: The selections to be used for the neighborhood enrichment score. A neighborhood enrichment score will be calculated for all possible names available in the selections.
- Radius: The selection radius will be used to calculate the connectivities of cells. For a given cell, every other cell that is closer than this selection radius will be considered as connected.
- Keep unassigned: If ticked (yes), all the cells from the cell segmentation will be used during the computation. The cells that are not part of the selections will be assigned to type NA ("Not Assigned") and will be included in the subsequent computation. If not ticked (no), cells that are not part of the selections will be ignored.
- Experiment name: A unique identifier for the current neighborhood enrichment run. With different experiment names, you will be able to see and compare the results from different neighborhood enrichment computations.
¶ Tissue microenvironment analysis
¶ Recurrent spatial neighborhoods (RCNs)
Recurrent cellular neighborhoods (RCN) are proposed as groups of cells (of possibly different types) that are representative of recurring patterns of cellular organization. RCNs differ from each other in terms of their cell type composition and when taken together define the tissue from a higher level of cellular organization. An important aspect of these RCNs is that they can correspond to biologically known functional tissue areas. Identifying a correspondence between a subset of RCNs and known tissue functions can suggest possible relations between the other RCNs (or a collection of them thereof) and unknown or novel tissue functions.
To start an RCN analysis click on the NEW JOB button and select RCN. To submit the RCN job, you need to provide the following parameters:
- Selections: The selections to be used for the recurrent neighborhood analysis. Resulting RCNs will be a combination of the names available in the selections.
- Radius: The selection radius will be used to calculate the cell neighborhoods. For a given cell, every other cell that is closer than this selection radius will be considered as a neighbor.
- Number of RCNs The number of recurrent cellular neighborhoods extracted from the sample. Each cell will be assigned to one of these neighborhoods.
- Keep unassigned: If ticked (yes), all the cells from the cell segmentation will be used during the computation. The cells that are not part of the selections will be assigned to type NA ("Not Assigned") and will be included in the subsequent computation. If not ticked (no), cells that are not part of the selections will be ignored.
- Experiment name: A unique identifier for the current recurrent neighborhood run. With different experiment names, you will be able to see and compare the results from different RCN computations.